Back to the news page
03.28.2017
The difference between OBD, auto and stationary TPMS relearns
What is TPMS?
The tire pressure monitoring system (TPMS) primary function is to make the driver aware of the state of tire pressure within
the wheels. Under normal system operations, the TPMS system will alert the driver when one or more affected tires PSI reading falls below 25% of the placard. When the tire sensor indicates “low tire pressure”, it sends an RF signal to the ECU on the vehicle that determines if the pressure is below the threshold, which then will indicate a TPMS symbol or position-specific display, depending on the vehicle.
Direct vs. Indirect TPMS systems
There are two types of TPMS systems: direct TPMS and indirect TPMS. Direct TPMS systems use TPMS sensors inside the wheel to report pressure data to the vehicle’s ECU in real time. Direct systems include Asian, Domestic and European vehicles. Direct systems are more accurate and reliable to indicate which tire is underinflated. An indirect TPMS system uses an ABS system to monitor the speed of the wheel and communicate to the ECU. Indirect systems include Asian and some European vehicles. Indirect systems are less reliable since they cannot tell the driver which tire is low on pressure, and won’t warn the driver if all four tires are losing pressure at the same time.
Types of relearn procedures
When a service has been performed to the direct TPMS system, such as air pressure adjustment, tire rotation or replacement of sensors, most vehicles will require a TPMS system relearn to be performed. Relearn procedures vary by manufacturer, so a technician must know if a relearn procedure is necessary to put the vehicle in “learn” mode. Although relearn procedures differ from manufacturer to manufacturer, the three types of relearn procedures are auto relearn, stationary and OBD. Furthermore, some vehicles may use a combination of two or more relearn types. Indirect TPMS systems use an initialization procedure which may require a TPMS tool to figure out the steps involved to reset the system.
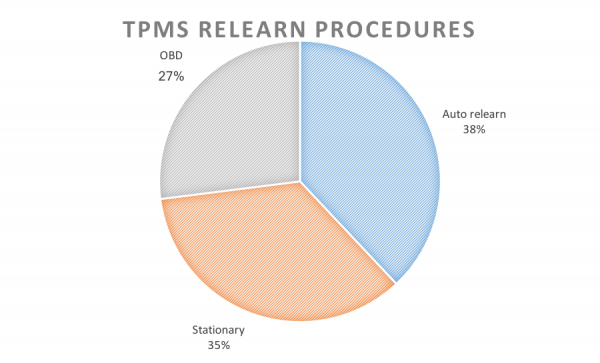
The chart below represents the three types of TPMS relearn procedures within the market of Asian, Domestic and European vehicles equipped with direct TPMS systems. (www.amra.org)
Note: The VT56 TPMS tool has relearn procedure instructions built in for relearn procedures; simply select SERVICE from the MAIN MENU, then select the vehicle’s MMY (make, model, year) or scan the vehicle’s VIN barcode. The tool will display the OBDII and/or manual relearn procedures step-by-step as well as a HELP guide if the technician runs into issues during the relearn procedure process. Instructions for indirect system procedures can also be found on the VT56.
the MAIN MENU, then select the vehicle’s MMY (make, model, year) or scan the vehicle’s VIN barcode. The tool will display the OBDII and/or manual relearn procedures step-by-step as well as a HELP guide if the technician runs into issues during the relearn procedure process. Instructions for indirect system procedures can also be found on the VT56.
Auto relearn procedure
An auto relearn procedure is when a vehicle has the ability to learn a single or multiple TPMS sensor IDs without the need of performing the procedure with a TPMS tool. Furthermore, a technician can adjust the inflation pressure, rotate or replace sensors and the TPMS system will reset itself after the vehicle has been driven for a period of time. Before servicing the tires/wheels, it is always recommended to use a TPMS tool to trigger each of the vehicle’s sensors to make sure they are working properly.
For example, a 2008 Dodge Charger requires an auto relearn procedure:
Stationary relearn procedure
A stationary (sometimes called manual) relearn procedure allows new TPMS sensor IDs to be transferred to the vehicle’s ECU without driving a vehicle. This type of relearn procedure requires a TPMS activation tool to trigger the sensors when the vehicle is in learn mode either by using a TPMS diagnostic tool or diagnostic scan tool. The vehicle then uses an RF signal to communicate with the vehicle’s ECU to establish which sensor is in which specific location.
For example, a 2014 Ford Escape (with standard ignition) requires a stationary relearn procedure:
OBDII relearn procedure
An OBDII relearn procedure requires a TPMS scan tool to transfer new sensor IDs directly to the vehicle’s ECU. The user would need to scan each TPMS sensor, connect to the vehicle’s OBD port, then follow the step-by-step instructions on the tool. The new TPMS sensor IDs are then transferred to the vehicle. Most Asian and specialty European vehicles require OBD relearn.
For example, a 2011 Toyota Camry requires an OBDII relearn procedure:

The importance of OBD relearn
Manual and stationary relearn systems can sometimes take several steps to relearn the TPMS system. TPMS tools, such as the VT56 tool, have the step-by-step instructions for auto, stationary and OBD relearn, however, the steps involved can be long and complicated. OBD relearn procedures are becoming standard in a shop environment for many reasons. First and foremost, it is the easier to work with since the same procedure can be performed no matter what the vehicle type is. Secondly, OBD relearn saves time and confusion for the technician since there are less steps to perform. At 86%, ATEQ has the largest percentage of OBD relearn protocols in their TPMS tools than any other TPMS tool company.
ATEQ is inviting visitors to explore its new global ...
The newest location is officially open for TPMS sale...
ATEQ TPMS Tools is proud to announce Desart Dinkolla...